This is an old revision of the document!
SPACAR Light
Example: Compute transfer function of a parallel flexure guide
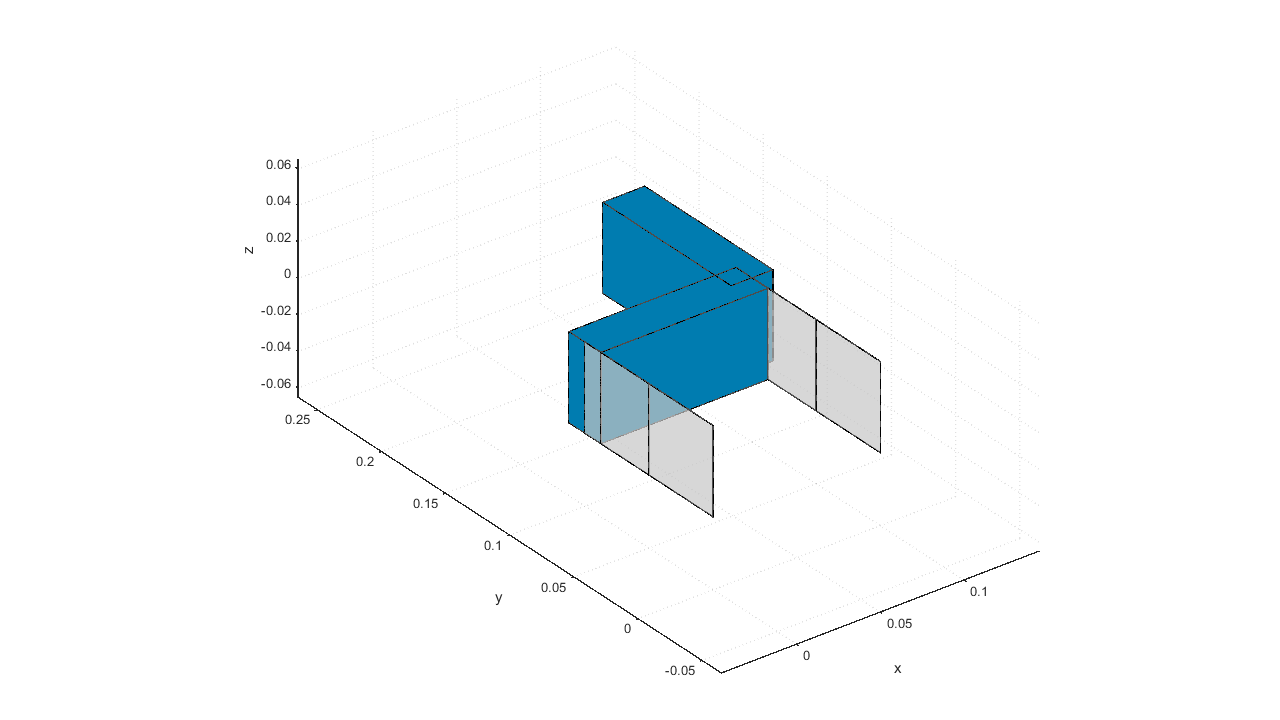
This example shows the computation of the transfer function from input actuator force (force in x-direction on the end-effector) to output stage displacement (motion in x-direction of the end-effector) of a parallel flexure guide.
The state-space equations (from which the transfer function follows) can be computed by specifying the input and output for the transfer function. For this example, actuation force in x-direction on node 3 (a node on the end-effector) is used for input, and displacement in x-direction of node 3 is used for the output. This can be specified with the nprops(i).transfer_in and nprops(i).transfer_out arguments. Furthermore, to enable the computation of the state-space equations, the optional field opt.transfer has to be set to true. For details, see the SPACAR Light full syntax. For this case, the MATLAB file that defines the flexure mechanism is supplemented with
nprops(3).transfer_in = {'force_x'}; %Input for state-space equations nprops(3).transfer_out = {'displ_x'}; %Output for state-space equations ... opt.transfer = {true 0.01}; %Calculation of state-space equations (with relative damping 0.01)
Note that
- the state-space equations can only be computed for an undeformed flexure mechanism. Therefore, no external loads (actuation force) or input displacements are allowed when computing state-space equations. (An error message will appear.)
- Velocity outputs are supported as well;
- Relative damping for all modes of the system can be specified optionally by means of the
opt.transferfield.
For details, see the SPACAR Light full syntax.
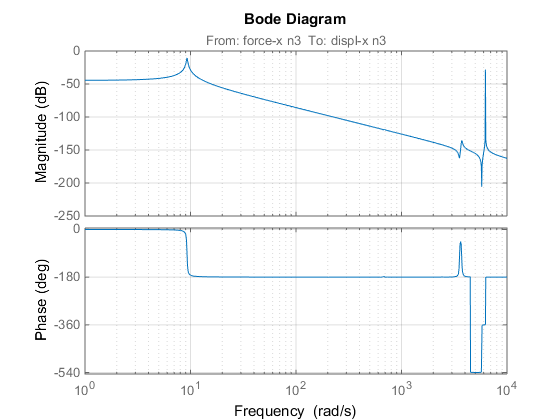
The resulting transfer function is plotted in the figure below. The first eigenfrequency is approximately 10 rad/s; the first parasitic eigenfrequency appears at 360 rad/s.
An example file for providing the input for SPACAR Light and plotting the transfer function is provided below.
- example.m
% EXAMPLE SCRIPT FOR RUNNING SPACAR LIGHT % This example simulates a parallel flexure guide and computes the transfer % function from actuator force to sensor displacement clear clc %% NODE POSITIONS % x y z nodes = [ 0 0 0; %node 1 0 0.1 0; %node 2 0.1 0.1 0; %node 3 0.1 0 0; %node 4 0.1 0.2 0]; %node 5 %% ELEMENT CONNECTIVITY % p q elements = [ 1 2; %element 1 2 3; %element 2 3 4; %element 3 3 5]; %element 4 %% NODE PROPERTIES %node 1 nprops(1).fix = true; %Fix node 1 %node 3 nprops(3).transfer_in = {'force_x'}; %Input for state-space equations nprops(3).transfer_out = {'displ_x'}; %Output for state-space equations %node 4 nprops(4).fix = true; %Fix node 4 %% ELEMENT PROPERTIES %Property set 1 eprops(1).elems = [1 3]; %Add this set of properties to elements 1 and 3 eprops(1).emod = 210e9; %E-modulus [Pa] eprops(1).smod = 70e9; %G-modulus [Pa] eprops(1).dens = 7800; %Density [kg/m^3] eprops(1).cshape = 'rect'; %Rectangular cross-section eprops(1).dim = [50e-3 0.2e-3]; %Width: 50 mm, thickness: 0.2 mm eprops(1).orien = [0 0 1]; %Orientation of the cross-section as a vector pointing along "width-direction" eprops(1).nbeams = 2; %2 beam elements for simulating these flexures eprops(1).flex = 1:6; %Fully flexible beam eprops(1).color = 'grey'; %Color of elements eprops(1).opacity = 0.7; %Opacity of elements eprops(1).cw = true; %Enable (approximate) torsional stiffening due to constraint warping %Property set 2 eprops(2).elems = [2 4]; %Add this set of properties to element 2 and 4 eprops(2).dens = 7800; %Density [kg/m^3] eprops(2).cshape = 'rect'; %Rectangular cross-section eprops(2).dim = [50e-3 25e-3]; %Width: 50 mm, thickness: 25 mm eprops(2).orien = [0 0 1]; %Orientation of the cross-section as a vector pointing along "width-direction" eprops(2).nbeams = 1; %1 beam element for simulating this component eprops(2).color = 'darkblue'; %Color of elements %% OPTIONAL ARGUMENTS opt.transfer = {true 0.01}; %Calculation of state-space equations (with relative damping 0.01) %% CALL SPACAR_LIGHT out = spacarlight(nodes, elements, nprops, eprops, opt); %% Plot transfer function figure bode(out.statespace,{1,10000}) grid minor